The Small Parts On A Mobile Phone’s PCB
In this article on “How To Identify Mobile Phone Parts/functions ” we shall be focusing on “The Small Parts” found on mobile phones generally before digging in to “The Big Parts“,
Most technicians who do not know how important it is to identify mobile phone parts/functions performed by each of these parts may not be able to achieve much and might even experience more damages or make avoidable mistakes by neglecting such an indispensable aspect of the art. Its so funny sometimes when you see some G.S.M Technicians doing a jumper connecting two points say from A to B where a a shorted capacitor or diode was removed. Such a thing should rather be done for a fuse in power section or where appropriate instead.
When you do jumper for a capacitor, you are creating an artificial short and adding more salt to the injury! You should rather do that for an open circuit where you are sure their is a broken path. Alright, that was just by the way. At this point, we will begin to consider how to identify mobile phone parts/functions they perform.
How To Identify Mobile Phone Parts/functions They Perform
Resistors: A solid state electronic component that resist or limit the flow of current in a 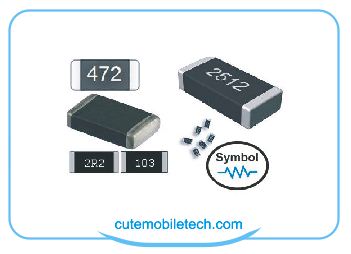 circuit to a measured value. It opposes the flow of current, and is measured in ohms using the multi-meter. When a resistor is open a phone can go dead. When the resistance value of a resistor drops say from 1.5 Kilo Ohms to 700 Ohms, then more current will flow into the circuit board and vice versa. Get a schematic or block diagrams to find out the exact value the manufacturer assigned so you can read on your PCB and check if it corresponds or needs to be changed. You can check the measurement using the multi-meter in Ohms mode. Resistors with 0 resistances will act like fuse, so they will give sound in buzzer mode while a 1kilo Ohms resistor will not give a buzzer sound in same mode. The values of resistors are written on them, but in cases where they are too small, the values are not written and are therefore left plane. However one can still know the resistance value using the ohms mode on the multi-meter.
circuit to a measured value. It opposes the flow of current, and is measured in ohms using the multi-meter. When a resistor is open a phone can go dead. When the resistance value of a resistor drops say from 1.5 Kilo Ohms to 700 Ohms, then more current will flow into the circuit board and vice versa. Get a schematic or block diagrams to find out the exact value the manufacturer assigned so you can read on your PCB and check if it corresponds or needs to be changed. You can check the measurement using the multi-meter in Ohms mode. Resistors with 0 resistances will act like fuse, so they will give sound in buzzer mode while a 1kilo Ohms resistor will not give a buzzer sound in same mode. The values of resistors are written on them, but in cases where they are too small, the values are not written and are therefore left plane. However one can still know the resistance value using the ohms mode on the multi-meter.
Capacitors: An electronic component that acts as filter by filtering electric current from either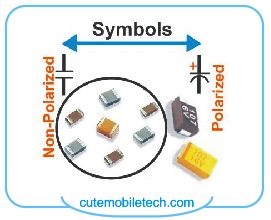 AC or DC source and creating stability and eliminating noise in a circuit. Capacitors can be either polarized or non-polarized. When working with a polarized capacitor, you will have to take the positive and the negative terminal into consideration by making sure they are placed according to the positive and the negative terminals. The non-polarized can be placed in any direction you like; they can be found in grey, brown and orange like colors. One can find the SMT polarized capacitors in two colors on mobile phones in black with a white strip representing negative, and orange color capacitor with a brown strip representing negative side. To know the value of a capacitor, its capacitance is measured using the capacitance meter. Depending on where the capacitor is found in a circuit, it can affect the proper functioning of those hardware components it is connected to. If charging capacitor is shorted for example, the phone won’t charge and chargers may get burnt amongst other things the phone can go dead too. A faulty capacitor will give sound in buzzer mode while a good one will not. You can also check if it’s good in battery mode. While set to 20 DCV if it keeps dropping in reading it’s a healthy sign. While set to Ohms mode say like 2000k, if it keeps increasing in reading, it’s a good sign
AC or DC source and creating stability and eliminating noise in a circuit. Capacitors can be either polarized or non-polarized. When working with a polarized capacitor, you will have to take the positive and the negative terminal into consideration by making sure they are placed according to the positive and the negative terminals. The non-polarized can be placed in any direction you like; they can be found in grey, brown and orange like colors. One can find the SMT polarized capacitors in two colors on mobile phones in black with a white strip representing negative, and orange color capacitor with a brown strip representing negative side. To know the value of a capacitor, its capacitance is measured using the capacitance meter. Depending on where the capacitor is found in a circuit, it can affect the proper functioning of those hardware components it is connected to. If charging capacitor is shorted for example, the phone won’t charge and chargers may get burnt amongst other things the phone can go dead too. A faulty capacitor will give sound in buzzer mode while a good one will not. You can also check if it’s good in battery mode. While set to 20 DCV if it keeps dropping in reading it’s a healthy sign. While set to Ohms mode say like 2000k, if it keeps increasing in reading, it’s a good sign
Diode: An electronic component that allow current flow in a particular direction; either  forward bias or reverse bias depending on the circumstances of the flow of current. The diode you will familiarize with in GSM repairs includes the following: Zenar diode, rectifier diode, photo diode and the light emitting diode known as the LED.
forward bias or reverse bias depending on the circumstances of the flow of current. The diode you will familiarize with in GSM repairs includes the following: Zenar diode, rectifier diode, photo diode and the light emitting diode known as the LED.
The Zener diode is found in the charging section and is responsible for filtering, protecting, minimizing and regulating current and passing it forward; it comes in different strength and values i.e. 4volts, 6volts, 8volts 10volts etc.
The rectifier diode on the other hand is found in power section and converts AC current into DC. It allows the flow of current in the one forward bias direction and not reverse bias like the zener diode.
The photo diode mainly senses and capture light rays for infrared functionality; by this means it is able to transfer data for a required user function. This application is found in sensors, remote controls and some high tech medical equipment.
The LEDs (Light Emitting Diode ) primarily emits or produces light. It is a crystal substance that produces light when current flows through it. The light color is determined by the crystal color combination. LEDs illuminate the phone’s screen display. You can test if the LED is good by using the both test leads of your multi-meter to check if it glows when in buzzer mode. Aside the diodes discoursed here; there are several other diodes like tunnel diode, shocky diode etc
Normally, a diode is tested in the buzzer mode. If it gives sound in buzzer mode, that is a bad sign that it is shorted and should be removed so that it doesn’t affect the functioning of any part of a phone’s smooth working. A good diode should read 1 in one direction and more than 1 in the other direction when you test with a multi-meter. A bad diode giving buzzer sound can affect any part of a phone. It can affect power, it can affect charging etc.
Transistor: A semi-conductor solid state electronic device. It’s a combination of two or more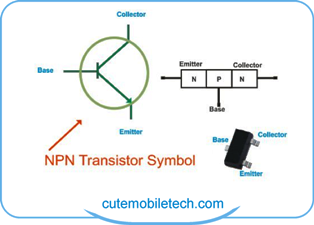 diode acting as switching mechanism in an electronic circuit. Generally speaking there are two main types of transistors namely the NPN transistors and the PNP transistors. A transistor consists of the base (B), the collector (C) and the emitter (E). Aside acting as a switch, it also performs amplification of electronic signals. The commonly used of the duo is the NPN, and this probably because it is easily made from silicon which is cheap and readily available. A good example of how it amplifies electronic signals is when you are about to snap a picture, you notice a sudden flash of LED light in its fullest strength! That’s the amplification function aspect. There are lots of them on the PCB and can be found in charging sections, power IC section, display IC sections etc.
diode acting as switching mechanism in an electronic circuit. Generally speaking there are two main types of transistors namely the NPN transistors and the PNP transistors. A transistor consists of the base (B), the collector (C) and the emitter (E). Aside acting as a switch, it also performs amplification of electronic signals. The commonly used of the duo is the NPN, and this probably because it is easily made from silicon which is cheap and readily available. A good example of how it amplifies electronic signals is when you are about to snap a picture, you notice a sudden flash of LED light in its fullest strength! That’s the amplification function aspect. There are lots of them on the PCB and can be found in charging sections, power IC section, display IC sections etc.
Coils: Coils may either be boost or step down coils depending on the function they perform 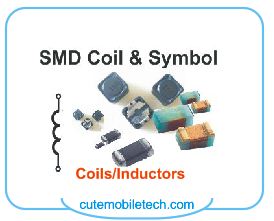 just like what you see in the case of AC to DC transformers. Boost coil can be found in any part of a phone’s PCB. They are required to step up current-voltage required for a specific function according to a measure of value while on the other hand, the step down coils helps to reduce and regulate the flow of current to a determined value. Step down coils usually supply current to ICs that function at low current-voltage level, this is why they are spread all across a phone’s PCB like the resistors and caps. A faulty coil could create and open thereby interrupting the value of current expected to flow through a circuit in a mobile phone’s PCB.
just like what you see in the case of AC to DC transformers. Boost coil can be found in any part of a phone’s PCB. They are required to step up current-voltage required for a specific function according to a measure of value while on the other hand, the step down coils helps to reduce and regulate the flow of current to a determined value. Step down coils usually supply current to ICs that function at low current-voltage level, this is why they are spread all across a phone’s PCB like the resistors and caps. A faulty coil could create and open thereby interrupting the value of current expected to flow through a circuit in a mobile phone’s PCB.
Backlight Driver: The backlight driver in a mobile phone supplies a regulated amount of  electric current needed for the phone LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) to be illuminated. The backlight driver has eight legs or pins and comes in different sizes and shapes and can be found in the power section of a mobile phone mostly close to the battery terminal. When the backlight driver is faulty the phone screen will go black and nothing will be visible in the display.
electric current needed for the phone LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) to be illuminated. The backlight driver has eight legs or pins and comes in different sizes and shapes and can be found in the power section of a mobile phone mostly close to the battery terminal. When the backlight driver is faulty the phone screen will go black and nothing will be visible in the display.
Related Articles:











Am really impressed with this thanks sir more wisdom
Bonsoir Mr Usman je viens de découvrir votre site internet qui est super important pour nous les débutants vraiment merci beaucoup
Thanks bro, your write ups leave me in laughter though
Thx bro
welcome
Thanks so much sir for this wonderful explanation, God bless you an grant you more wisdom
@Samson, Glade you liked it….
This is rich, I love it. Weldon